Grounded.
In a “solidly grounded” electrical system supplied by an electrical utility company, one of the derived conductors on the secondary side of the utility transformer is intentionally grounded (connected to earth). This is the “grounded conductor” for an electrical service supplied by the utility transformer.
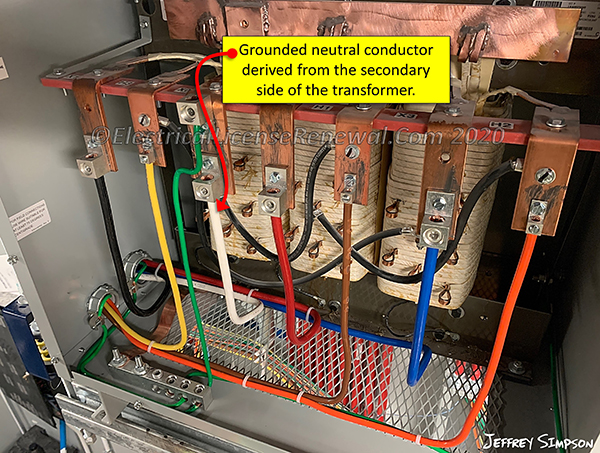
The same principle applies when a customer owned step-down transformer is installed downstream of an electrical service and a grounded conductor is derived from the secondary side of the transformer. This example describes a separately derived system.
Article 100 defines a separately derived system as follows:
Separately Derived System. An electrical source, other than a service, having no direct connection(s) to circuit conductors of any other electrical source other than those established by grounding and bonding connections.
In the typical dry-type, 480/277 Wye 3-phase step-down transformer installation, three phase conductors supply the primary side of the transformer. The primary and secondary windings of the transformer have no physical connection to each other. Through impedance, secondary conductors of a lesser voltage and a grounded conductor (usually a neutral conductor) are derived. Three conductors supply the primary side of the transformer and four conductors (one being a grounded neutral) come out of the secondary side.
In the above example, the grounded conductor connects to a grounding terminal inside the transformer and a grounding electrode conductor then joins the grounding busbar inside the transformer to the grounding electrode for the building. The grounded neutral conductor provides a current return path for anything utilizing a neutral supplied from the secondary side of the transformer and also provides an effective ground-fault current path in case a fault to ground occurs downstream of the transformer. An effective ground-fault current path is critical to ensure that an overcurrent device opens (trips) during a ground-fault condition.
Below is a preview of the NEC®. See the actual NEC® text at NFPA.ORG for the complete code section. Once there, click on their link to free access to the 2020 NEC® edition of NFPA 70.
Article 100 Definitions:
Grounded (Grounding). Connected (connecting) to ground or to a conductive body that extends the ground connection.
Grounded Conductor. A system or circuit conductor that is intentionally grounded.
Informational Note: Although an equipment grounding conductor is grounded, it is not considered a grounded conductor.
Grounded, Solidly. Connected to ground without inserting any resistor or impedance device.