250.104(A) Metal Water Piping.
Code Change Summary: Revised code language on bonding metal water piping systems.
According to NEC® 250.52(A)(1), metal underground water piping that is electrically continuous and in direct contact with the earth for at least 10 feet qualifies as a grounding electrode.
The grounding electrode conductor between the water pipe grounding electrode mentioned above and the service is sized from NEC® Table 250.66 which never requires larger than 3/0 copper or 250 kcmil aluminum.
Since the 2014 NEC®, Table 250.66 has only applied to grounding electrode conductors. Prior to that, Table 250.66 was used to size other items including grounding electrode conductors, grounded conductors, main bonding jumpers, system bonding jumpers, supply-side bonding jumpers and bonding jumpers to other metal water piping that did not qualify as a grounding electrode.
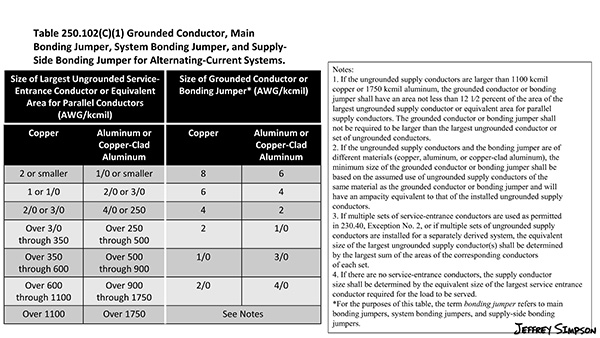
The bonding jumper from the service to other metal water piping not meeting the criteria in 250.52(A)(1) is currently sized from NEC® Table 250.102(C)(1) but in the 2014 NEC®, was sized from Table 250.66 and never had to be larger than 3/0 copper or 250 kcmil aluminum.
In the 2017 NEC®, a proposal was accepted to change a code reference in 250.104(A)(1) which resulted in a bonding jumper to other metal water piping having to be sized using the same method for other items in Table 250.102(C)(1) using the 12 ½% rule (from note 2 under the table) when the largest ungrounded conductor exceeded 1100 kcmil copper or 1750 kcmil aluminum.
In the 2020 NEC®, this mistake was corrected and now, a bonding jumper to other metal water piping (that does not qualify as a grounding electrode) is never required to be larger than 3/0 copper or 250 kcmil aluminum.
Below is a preview of the NEC®. See the actual NEC® text at NFPA.ORG for the complete code section. Once there, click on their link to free access to the 2020 NEC® edition of NFPA 70.
2017 Code Language:
250.104(A)(1) General. Metal water piping system(s) installed in or attached to a building or structure shall be bonded to any of the following:
(1) Service equipment enclosure
(2) Grounded conductor at the service
(3) Grounding electrode conductor if of sufficient size
(4) One or more grounding electrodes used, if the grounding electrode conductor or bonding jumper to the grounding electrode is of sufficient size 250.102(C)(1) except as permitted in 250.104(A)(2) and 250.104(A)(3).
The bonding jumper(s) shall be installed in accordance with 250.64(A), 250.64(B), and 250.64(E). The points of attachment of the bonding jumper(s) shall be accessible. The bonding jumper(s) shall be sized in accordance with Table
2020 Code Language:
250.104(A)(1) General. Metal water piping system(s) installed in or attached to a building or structure shall be bonded to any of the following:
(1) Service equipment enclosure
(2) Grounded conductor at the service
(3) Grounding electrode conductor, if of sufficient size
(4) One or more grounding electrodes used, if the grounding electrode conductor or bonding jumper to the grounding electrode is of sufficient size
The bonding jumper(s) shall be installed in accordance with 250.64(A), 250.64(B), and 250.64(E). The points of attachment of the bonding jumper(s) shall be accessible. The bonding jumper(s) shall be sized in accordance with Table 250.102(C)(1) except that it shall not be required to be larger than 3/0 copper or 250 kcmil aluminum or copper-clad aluminum and except as permitted in 250.104(A)(2) and 250.104(A)(3).