250.66 Grounding Electrode Conductor for Alternating Current Systems.
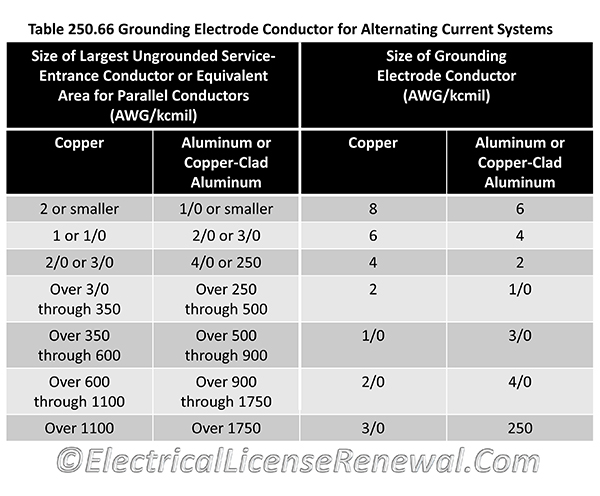
NEC Table 250.66 is used for sizing grounding electrode conductors for alternating current systems. As defined in Article 100, the Grounding Electrode Conductor is used to connect the system grounded conductor or the equipment to a grounding electrode or to a point on the grounding electrode system.
The grounding electrode conductor is not intended to carry current under normal conditions but it provides a path to the grounding electrode in order to limit voltage caused by things like lightning, power line surges, or unintentional contact with higher-voltage lines. Since the grounding electrode conductor is not meant to carry current normally, it is sized differently than other current-carrying conductors using NEC® Table 250.66.
When using the table, the size of a grounding electrode conductor is determined based on the size of the service entrance conductors. Sometimes, the utility installs the service entrance conductors after the electrician is finished and the electrician has no clue what size service entrance conductors will be installed.
Note 2 under Table 250.66 makes it clear that if there are no service-entrance conductors, “the grounding electrode conductor size shall be determined by the equivalent size of the largest service-entrance conductor required for the load to be served”.
For complete code sections, refer to the actual NEC® text at NFPA.ORG. Once there, click on their link to free access to the 2017 NEC® edition of NFPA 70.