705.25(B) Wiring Methods.
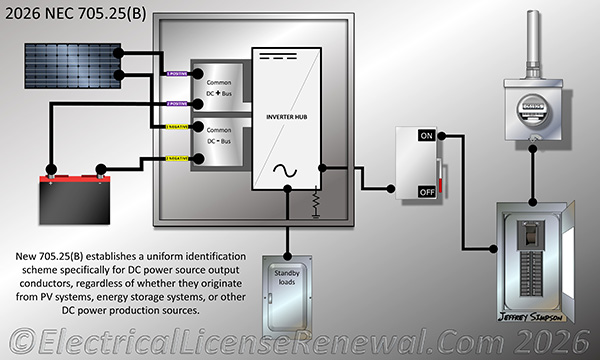
New 705.25(B) establishes a uniform identification scheme specifically for DC power source output conductors, regardless of whether they originate from PV systems, energy storage systems, or other DC power production sources.
Code Change Summary: A new subsection was added to establish identification requirements for dc power source output conductors.
SME commentary: The 2026 NEC® introduced new circuit identification requirements in 705.25(B) to address a gray area that existed for DC conductors associated with power production sources interconnected to operate in parallel with the normal source of supply. Prior editions of the Code relied heavily on the grounded conductor identification requirements in Article 200 for solidly grounded systems, and the DC branch circuit conductor identification language in Article 210. In most installations, DC power source output conductors are functionally grounded through a resistor rather than solidly grounded. Likewise, these DC circuits do not technically meet the Article 100 definition of a “branch circuit” because they are not the conductors between the final overcurrent protective device and the outlets served. As a result, applying Article 210 branch circuit identification rules to DC power source conductors created confusion, particularly in DC coupled hybrid systems where multiple DC sources terminate within the same equipment or enclosure.
The accepted substantiation from the PV Industry Forum highlights this issue clearly. Modern power production systems often combine multiple DC sources such as photovoltaic arrays and battery energy storage systems. These systems are frequently non-solidly grounded, they are functionally grounded and interconnected through the same ground-fault protection device. Under the 2023 NEC® structure, PV DC circuit identification was addressed in 690.31(B)(2), while other DC systems such as energy storage, charge controllers, and the DC input connections to hybrid inverters fell under other Articles such as 706, 480, or 710. Those articles did not provide comparable DC conductor identification rules, which forced installers and inspectors to default back to Article 200 grounded conductor color rules, and the identification requirements for DC branch circuits in Article 210 that technically do not apply to these conductors.
This created inconsistent and sometimes conflicting results. In a DC-coupled hybrid system, two or more DC power source circuits could enter the same inverter or enclosure with identical grounding characteristics but different color identification requirements. For example, functionally grounded DC PV conductors were prohibited by 690.31(B)(2) from using white, gray, or green, while battery system or DC ESS conductors could default to white or gray for one DC conductor under Article 200. This inconsistency increased the risk of misidentification during installation, inspection, or servicing.
New 705.25(B) resolves this by establishing a uniform identification scheme specifically for DC power source output conductors, regardless of whether they originate from PV systems, energy storage systems, or other DC power production sources. These rules apply at all termination, connection, and splice points:
For positive polarity, identification can include imprinted plus signs (+) or the word POSITIVE or POS durably marked on conductor insulation. Also acceptable is an approved permanent marking means like sleeving or shrink-tubing that is suitable for the conductor size at all termination, connection, and splice points, with imprinted plus signs (+) or the word POSITIVE or POS.
For negative polarity, identification can include imprinted minus signs (–) or the word NEGATIVE or NEG durably marked on conductor insulation. Also acceptable is an approved permanent marking means (e.g., sleeving or shrink-tubing) that is suitable for the conductor size at all termination, connection, and splice points, with imprinted minus signs (–) or the word NEGATIVE or NEG.
Where color is used, identification shall occur by one of the following means:
(1) For nonsolidly grounded dc positive conductors, marked with an insulation color other than green, white, or gray
(2) For nonsolidly grounded dc negative conductors, marked with an insulation color other than green, white, gray, or red
(3) For solidly grounded dc conductors, marked in accordance with 200.7
By placing these requirements in Article 705, the Code aligns DC conductor identification with the functional realities of modern power production systems. This change harmonizes markings across interconnected DC systems, improves consistency between PV and non-PV installations, and reduces ambiguity for installers and inspectors.
Below is a preview of the NEC®. See the actual NEC® text at NFPA.ORG for the complete code section. Once there, click on their link to free access to the 2026 NEC® edition of NFPA 70.
2023 Code Language:
This code section did not exist.
2026 Code Language:
N 705.25(B) Identification of dc Power Source Output Conductors. Color coding, marking tape, tagging, or other approved means in accordance with 705.25(B)(1) through 705.25(B)(3) shall be used to identify dc power source output conductors at all termination, connection, and splice points.
(1) Positive Polarity. Identification of dc positive conductors shall occur by one of the following means:
(1) Imprinted plus signs (+) or the word POSITIVE or POS durably marked on conductor insulation
(2) An approved permanent marking means (e.g., sleeving or shrink-tubing) that is suitable for the conductor size at all termination, connection, and splice points, with imprinted plus signs (+) or the word POSITIVE or POS
(2) Negative Polarity. Identification of dc negative conductors shall occur by one of the following means:
a. Imprinted minus signs (–) or the word NEGATIVE or NEG durably marked on conductor insulation
b. An approved permanent marking means (e.g., sleeving or shrink-tubing) that is suitable for the conductor size at all termination, connection, and splice points, with imprinted minus signs (–) or the word NEGATIVE or NEG
(3) Color Identification. Where color is used, identification shall occur by one of the following means:
(1) For nonsolidly grounded dc positive conductors, marked with an insulation color other than green, white, or gray
(2) For nonsolidly grounded dc negative conductors, marked with an insulation color other than green, white, gray, or red
(3) For solidly grounded dc conductors, marked in accordance with 200.7