555.14(A) Equipotential Plane Construction.
Several construction options are provided for the equipotential plane in 555.14(A).
Code Change Summary: Section 555.14 was revised to include detailed construction requirements for equipotential planes in marinas, boatyards, floating buildings, and docking facilities.
SME commentary: In the 2026 NEC®, Section 555.14(A) was expanded to provide specific construction requirements for equipotential planes used in marinas, boatyards, floating buildings, and docking facilities. Equipotential planes are defined in Article 100 as “conductive elements that are connected together to minimize voltage differences.” In these waterfront environments, equipotential planes are essential for reducing the risk of electrical shock to personnel who may simultaneously contact conductive surfaces and earth, particularly in wet or submerged areas.
Previously, Section 555.14(A) required equipotential planes but gave no instruction on how the plane itself was to be constructed. The 2026 revision resolves this by prescribing acceptable materials and installation methods, providing installers and inspectors with the detail needed for proper design and enforcement.
The new language mirrors the equipotential plane construction requirements added in other NEC® sections, such as 547.44(C) for agricultural buildings, and includes four recognized methods of compliance:
- Structural reinforcing steel. Unencapsulated structural reinforcing steel (rebar) is permitted and shall be bonded together by steel tie wires or the equivalent.
- A copper grid. Copper grids are permitted when constructed of minimum 8 AWG bare solid copper conductors bonded at all points of crossing in accordance with 250.8 or other approved means, arranged in a 12-inch by 12-inch uniformly spaced perpendicular grid pattern with a tolerance of 4 inches, and assembled using only listed splicing devices or exothermic welding.
- Unencapsulated welded wire. Unencapsulated steel structural welded wire reinforcement (welded wire mesh) is permitted if bonded together by steel tie wires or the equivalent and fully embedded within the surface material.
- Nonconductive surface provisions. If there is no structural reinforcing steel (rebar), or if the rebar is encapsulated in a nonconductive compound or if embedding is impossible, a copper conductor grid in accordance with 555.14(A)(2) must be provided directly under the surface material not more than 6 inches below finished grade.
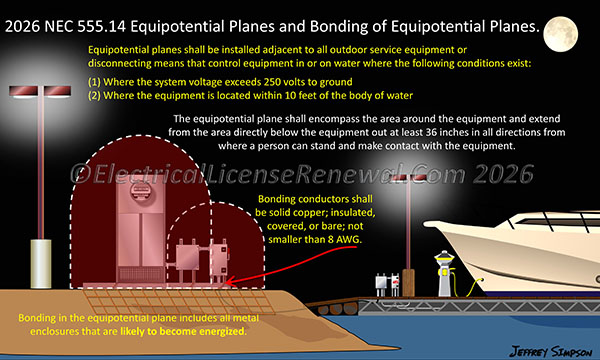
Revised Section 555.14(A) still maintains that the equipotential plane must encompass the area around outdoor service equipment or disconnecting means and extend outward from the area directly below the equipment not less than 36 inches in all directions from where personnel can stand and come in contact with the equipment.
This coordinated revision intends to bring Section 555.14 into alignment with similar equipotential plane language in 547.44(C), 680.26, and 682.33, which apply to agricultural, pool, and body-of-water installations. By standardizing construction details across these environments, the 2026 NEC® strengthens shock protection practices in areas where water and conductive materials coexist, improving both electrical safety and compliance consistency in marina and docking applications.
Below is a preview of the NEC®. See the actual NEC® text at NFPA.ORG for the complete code section. Once there, click on their link to free access to the 2026 NEC® edition of NFPA 70.
2023 Code Language:
Section 555.14(A) did not previously contain information on equipotential plane construction.
2026 Code Language:
555.14(A) Equipotential Plane Construction. Equipotential planes shall encompass the area around outdoor service equipment or disconnecting means and extend from the area directly below the equipment out not less than 36 inches in all directions from which a person would be able to stand and come in contact with the equipment. Bonding to equipotential planes shall be provided as specified in 555.14(A)(1) through 555.14(A)(4) and be attached to metallic enclosures that are likely to become energized with a solid copper conductor, insulated, covered or bare, and not smaller than 8 AWG.
N (1) Structural Reinforcing Steel. Unencapsulated structural reinforcing steel shall be bonded together by steel tie wires or the equivalent.
N (2) Copper Grid. Copper grid shall comply with the following requirements:
(1) Be constructed of minimum 8 AWG bare solid copper conductors bonded to each other at all points of crossing in accordance with 250.8 or other approved means
(2) Be arranged in a 12 inch by 12 inch network of conductors in a uniformly spaced perpendicular grid pattern with a tolerance of 4 inches
(3) Be constructed using only listed splicing devices or exothermic welding
N (3) Unencapsulated Welded Wire. Unencapsulated steel structural welded wire reinforcement, bonded together by steel tie wires or the equivalent and fully embedded within the surface material, shall be permitted.
N (4) Nonconductive Surfaces. If structural reinforcing steel is absent or encapsulated in a nonconductive compound or if embedding is not possible, a copper conductor grid in accordance with 555.14(A)(2) shall be provided directly under the surface material not more than 6 inches below finished grade.
(B) Areas Not Requiring Equipotential Planes. Equipotential planes shall not be required for the controlled utilization equipment on the docking facility or floating building supplied by the service equipment or disconnecting means.