Article 100 Definitions. Transformer Secondary Conductor.
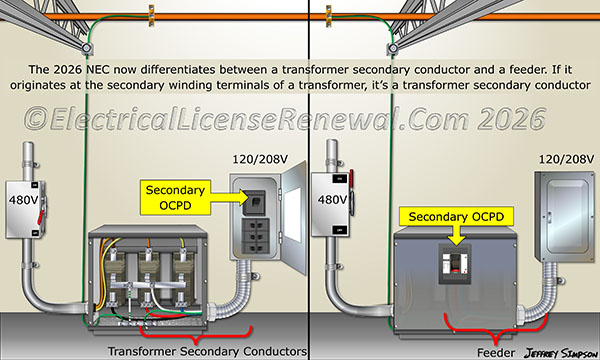
Transformer Secondary Conductors, versus a feeder.
Code Change Summary: New definition of a transformer secondary conductor.
SME commentary: In the 2026 NEC® a new definition of a “Transformer Secondary Conductor” was added to Article 100 to help differentiate between the conductors connected to the secondary of a transformer, “transformer secondary conductor”, and a “feeder”.
According to the new 2026 NEC® definition, a Transformer Secondary Conductor is “a conductor, other than a service conductor, that originates at the secondary winding terminals of a transformer”.
Article 100 defines a “Feeder” as all circuit conductors between the service equipment, the source of a separately derived system, or other power supply source and the final branch-circuit overcurrent protective device (OCPD).
Not all transformers are separately derived systems (see definition of a Separately Derived System for further information). The Article 100 definition of a feeder is general in nature. It’s about the circuit conductor itself and doesn’t get into detail on where the line-side overcurrent protection is located. Those rules are found elsewhere in the NEC®.
Some newer transformers are equipped from the factory with one or more integral circuit breakers providing primary overcurrent protection, secondary overcurrent protection, or both for the installation. Based on the new definition, conductors connected to the load side of an integral secondary overcurrent protective device (OCPD) in a transformer are considered “feeders”, not “Transformer Secondary Conductors”.
Note: Many transformers have an integral Molded Case Switch (not the same as an overcurrent device) that does not have an interrupting rating and is not intended to provide overcurrent protection to the transformer secondary conductors.
There are many NEC® code sections providing requirements pertaining to “transformer secondary conductors”. These rules have one thing in common; they all provide unique requirements for the conductors based on how and where the conductors are protected. Once the transformer secondary conductors land on an overcurrent device, and continue on from there to the distribution equipment containing the branch circuit overcurrent devices, the conductors are considered a “feeder” and the rules in the NEC® pertaining to feeders apply.
This code revision was driven by Public Input 3631, which pointed out that the term is used in at least 13 different NEC® sections without a formal definition. With newer transformer designs incorporating internal secondary OCPDs, this definition helps eliminate ambiguity and ensures that conductors are properly classified and the appropriate Code rules are applied.
Below is a preview of the NEC®. See the actual NEC® text at NFPA.ORG for the complete code section. Once there, click on their link to free access to the 2026 NEC® edition of NFPA 70.
2023 Code Language:
The definition did not exist.
2026 Code Language:
N Transformer Secondary Conductor. A conductor, other than a service conductor, that originates at the secondary winding terminals of a transformer.