690.12(B) Controlled Limits.
Code Change Summary: Revised requirements on PV system rapid shutdown and hazard control inside the array boundary.
In the 2020 NEC®, the language covering rapid shutdown inside the array boundary was revised to address PV Hazard Control Systems (PVHCS). These systems are within the scope of UL 3741 which is the Standard for Photovoltaic Hazard Control.
Section 690.4(B) requires PV rapid shutdown equipment (PVRSE), PV hazard control equipment (PVHCE), and PV hazard control systems intended for use in PV systems to be listed or be evaluated for the application and have a field label applied.
Section 690.12(B)(2) provides requirements to ensure electrical safety for first responders once the PVHCS has been initiated.
Firefighters often arrive to a fire and immediately kill all power to the building so they can safely employ rooftop procedures such as ventilating the roof to release smoke and heat which increases the survival chance of potential victims still inside the building.
A roof-mounted PV system can create a hazard for a fire fighter employing rooftop procedures. Firefighters have no desire to cut through the roof into live DC PV circuits that may be energized after the power has been disconnected to a building.
PV hazard control and rapid shutdown is critical to ensure that live DC conductors are reduced to a low enough voltage level that a firefighter cutting into a roof and contacting a PV system circuit is not exposed to a substantial shock hazard.
In the 2020 NEC®, there were three options to comply with the rapid shutdown control limits required inside the array boundary as specified in 690.12(B)(2):
- Install a PV hazard control system listed for the purpose.
- Limit the controlled conductors inside the array boundary to not more than 80 volts within 30 seconds of rapid shutdown initiation.
- Install the PV arrays so that they have no exposed wiring methods or conductive parts and install them more than 8 feet from exposed grounded conductive parts or ground.
In the 2023 NEC®, the first rule in 690.12(B)(2)(1) was revised to make it clear that the shock hazard control method is “for firefighters”, through the use of a PVHCS.
The second rule in 690.12(B)(2)(2) is also for firefighters and was made more precise by clarifying that the voltage limitation applies “inside” the equipment that is located within the boundary. The previous wording didn’t specify.
The third rule previously in 690.12(B)(2)(3) was deleted leaving only options 1, and 2 as acceptable methods of compliance.
Below is a preview of the NEC®. See the actual NEC® text at NFPA.ORG for the complete code section. Once there, click on their link to free access to the 2023 NEC® edition of NFPA 70.
2020 Code Language:
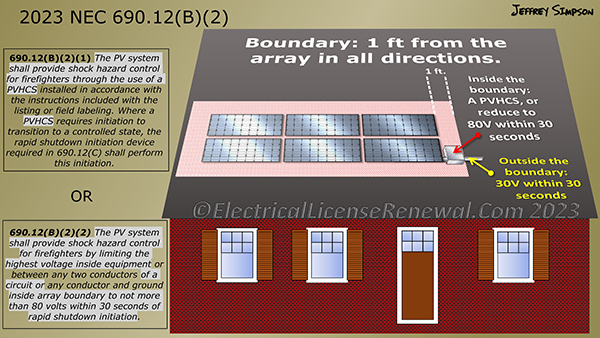
690.12(B) Controlled Limits. The use of the term array boundary in this section is defined as 1 foot from the array in all directions. Controlled conductors outside the array boundary shall comply with 690.12(B)(1) and inside the array boundary shall comply with 690.12(B)(2).
(2) Inside the Array Boundary. The PV system shall comply with one of the following:
(1) A PV hazard control system listed for the purpose shall be installed in accordance with the instructions included with the listing or field labeling. Where a hazard control system requires initiation to transition to a controlled state, the rapid shutdown initiation device required in 690.12(C) shall perform this initiation.
(2) Controlled conductors located inside the boundary shall be limited to not more than 80 volts within 30 seconds of rapid shutdown initiation. Voltage shall be measured between any two conductors and between any conductor and ground.
(3) PV arrays shall have no exposed wiring methods or conductive parts and be installed more than 8 feet from exposed grounded conductive parts or ground.
2023 Code Language:
690.12(B) Controlled Limits. The use of the term array boundary in this section is defined as 1 foot from the array in all directions. Controlled conductors outside the array boundary shall comply with 690.12(B)(1) and inside the array boundary shall comply with 690.12(B)(2). Equipment and systems shall be permitted to meet the requirements of both inside and outside the array as defined by the manufacturer's instructions included with the listing.
(2) Inside the Array Boundary. The PV system shall comply with one of the following:
(1) The PV system shall provide shock hazard control for firefighters through the use of a PVHCS installed in accordance with the instructions included with the listing or field labeling. Where a PVHCS requires initiation to transition to a controlled state, the rapid shutdown initiation device required in 690.12(C) shall perform this initiation.
(2) The PV system shall provide shock hazard control for firefighters by limiting the highest voltage inside equipment or between any two conductors of a circuit or any conductor and ground inside array boundary to not more than 80 volts within 30 seconds of rapid shutdown initiation.
Informational Note No. 2: Common methods include the use of PV equipment with a limited maximum voltage of 80 volts as determined by 690.7, PVRSE, PVHCE, or any combination of these.