430.52 Motor Branch-Circuit Short-Circuit and Ground-Fault Protection.
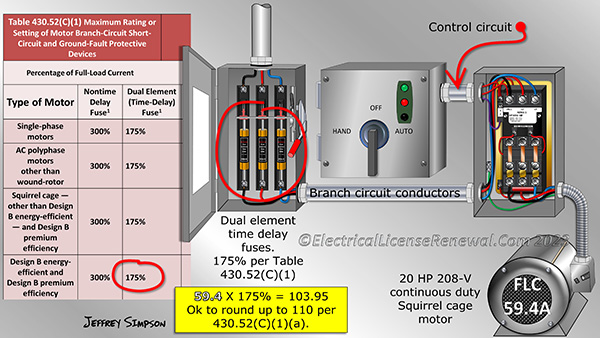
Section 430.52(C)(1) is used when determining the maximum overcurrent device (OCPD) permitted to protect the motor and branch circuit conductors. This section includes Table 430.52(C)(1) which contains percentages to be multiplied against the full load current (FLC) of the motor in order to find the maximum allowable OCPD.
The percentages in the table vary depending on which type of OCPD will be used for the installation.
When applying the percentages, if the result does not correspond with a standard size OCPD listed in Table 240.6(A), then 430.52(C)(1)(a) allows the next standard size OCPD to be used (ok to round up to the next size fuse or circuit breaker).
If the motor will not start without tripping the OCPD because of the initial inrush of current, 430.52(C)(1)(b) allows greater variations from the percentages shown in the table depending on which type of OCPD is used for the installation. These values cannot be exceeded when the result of using the larger percentages lands between standard OCPD sizes shown in Table 240.6(A). There is no provision to round up even further to the next standard size OCPD as permitted in 430.52(C)(1)(a).
See the actual NEC® text at NFPA.ORG for the complete code section. Once there, click on their link to free access to NFPA 70.